ECOHYDROLOGICAL ANALYSES IN THE LOWLAND RIVER CATCHMENT KIELSTAU, GERMANY, FOR SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND EDUCATION IN RURAL LANDSCAPES (GERMANY)

Description
Location


Sketch

Information about lithology/geochemistry:
Landscape mainly formed by the last ice age Soils: Stagnic and Haplic Luvisols, Stagnic Gleysols, Sapric Histosols
Main Description
- The rural Kielstau catchment (50 km²) is located in northern Germany in a lowland area.
- The Kielstau river’s water quality is strongly influenced by agriculture. Land use is dominated by grain, corn, rape and pasture; 38% of agricultural land is artificially drained (Fig.1).
- The Kielstau river is part of the flora fauna habitat directive (92/43/CEE), and nature conservation areas are used for moderate grazing.
Enhance ecohydrological processes in novel ecosystem
YES
Apply complementary Ecohydrological processes in high impacted system
YES
This table presents the different categories of ecosystem services that ecosystem can provide, divided in:
Provisioning Services are ecosystem services that describe the material or energy outputs from ecosystems. They include food, water and other resources.

Food: Ecosystems provide the conditions for growing food. Food comes principally from managed agro-ecosystems but marine and freshwater systems or forests also provide food for human consumption. Wild foods from forests are often underestimated.

Raw materials: Ecosystems provide a great diversity of materials for construction and fuel including wood, biofuels and plant oils that are directly derived from wild and cultivated plant species.
Regulating Services are the services that ecosystems provide by acting as regulators eg. regulating the quality of air and soil or by providing flood and disease control.

Erosion prevention and maintenance of soil fertility: Soil erosion is a key factor in the process of land degradation and desertification. Vegetation cover provides a vital regulating service by preventing soil erosion. Soil fertility is essential for plant growth and agriculture and well functioning ecosystems supply the soil with nutrients required to support plant growth.
Ecosystem services "that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services". These include services such as nutrient recycling, primary production and soil formation.

Habitats for species: Habitats provide everything that an individual plant or animal needs to survive: food; water; and shelter. Each ecosystem provides different habitats that can be essential for a species’ lifecycle. Migratory species including birds, fish, mammals and insects all depend upon different ecosystems during their movements.
Cultural Services corresponds nonmaterial benefits people obtain from ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, reflection, recreation, and aesthetic experiences.
Lifezones

![]()
PPT(mm/yr): 893.0
![]()
T(ºc): 8.3
| Elevation of demosite: | 53.0 meters above sea level |
| Humidity: | Humid |
| PETr (by year): | 0.55 |
EH Principles
Quantification of the hydrological processes at catchment scale and mapping the impacts
Distribution of ecosystems and their relevant processes (ex: metabolism=water and nutrient uptake and retention; biomass production)
Ecological engineering (integration, dual regulation and biotechnologies in catchment scale for enhancement of ecological potential)
ECOHYDROLOGY ENGINEERING SOLUTIONS
Renaturalisation of river sections and riparian wetlands
 Phytotechnology
Phytotechnology
River basin model; Hydraulic models; Species distribution model (SWAT; HEC-RAS; ADH; BIOMOD)
 Hydrological Flow
Hydrological Flow
Building and testing of reactive ditches (Fig.2) and retention ponds
 Ecohydrological Infrastructure
Ecohydrological Infrastructure
Major Issues
- Ecological status of the stream needs to be improved
- Nutrient (nitrogen and phosphorus) and pesticide loads due to agricultural activities



Expected Outcomes
Implementation of monitoring strategies and GIS-based approaches in a rural lowland river catchment
Blueprint for other rural basins
Latest Results
- There is a strong impact of shallow groundwater with intensive interactions between groundwater and surface water. Due to artificial drainage systems, the area is influenced by fast water transport (Schmalz et al., 2008, Kiesel et al., 2010, Pfannerstill et al., 2014).
- Integrated ecohydrological modelling by using hydrologic, hydraulic and biological data helps assessing aquatic habitats and ecosystems (Kiesel et al., 2009, 2013, 2015). A moderate ecological status was calculated by using biological indicators (Wu et al., 2012).
Contacts
Britta Schmalz
- bschmalz@hydrology.uni-kiel.de
- http://www.uni-kiel.de/
- Institute for Natural Resource Conservation, Kiel University
- http://www.uni-kiel.de/
Nicola Fohrer
- nfohrer@hydrology.uni-kiel.de
- http://www.uni-kiel.de/
- Institute for Natural Resource Conservation, Kiel University
- http://www.uni-kiel.de/
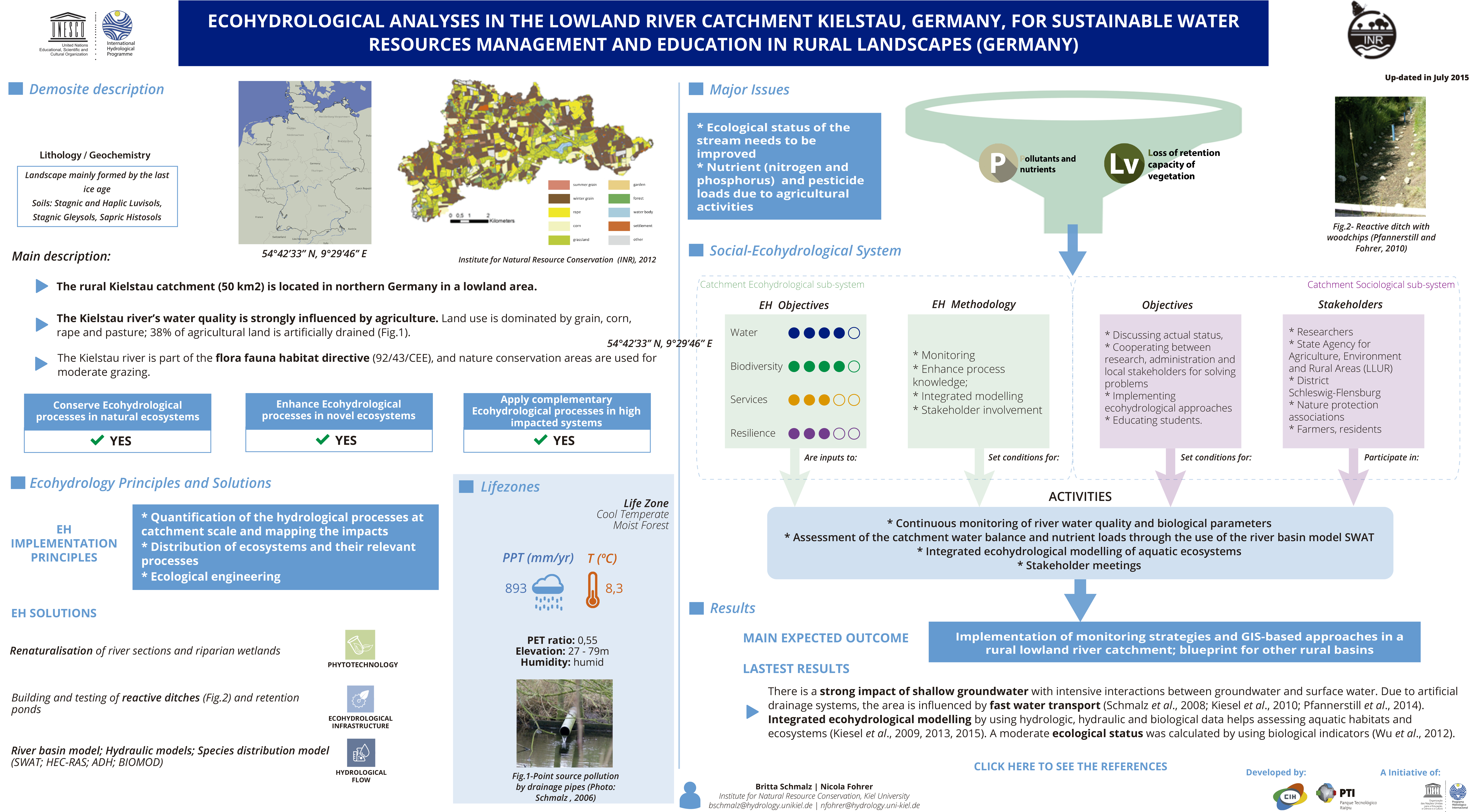
Social ecohydrological system
EH Objectives
EH Methodology
Catchment Ecohydrological sub-system
Objectives
Stakeholders
Catchment Sociological sub-system
Activities