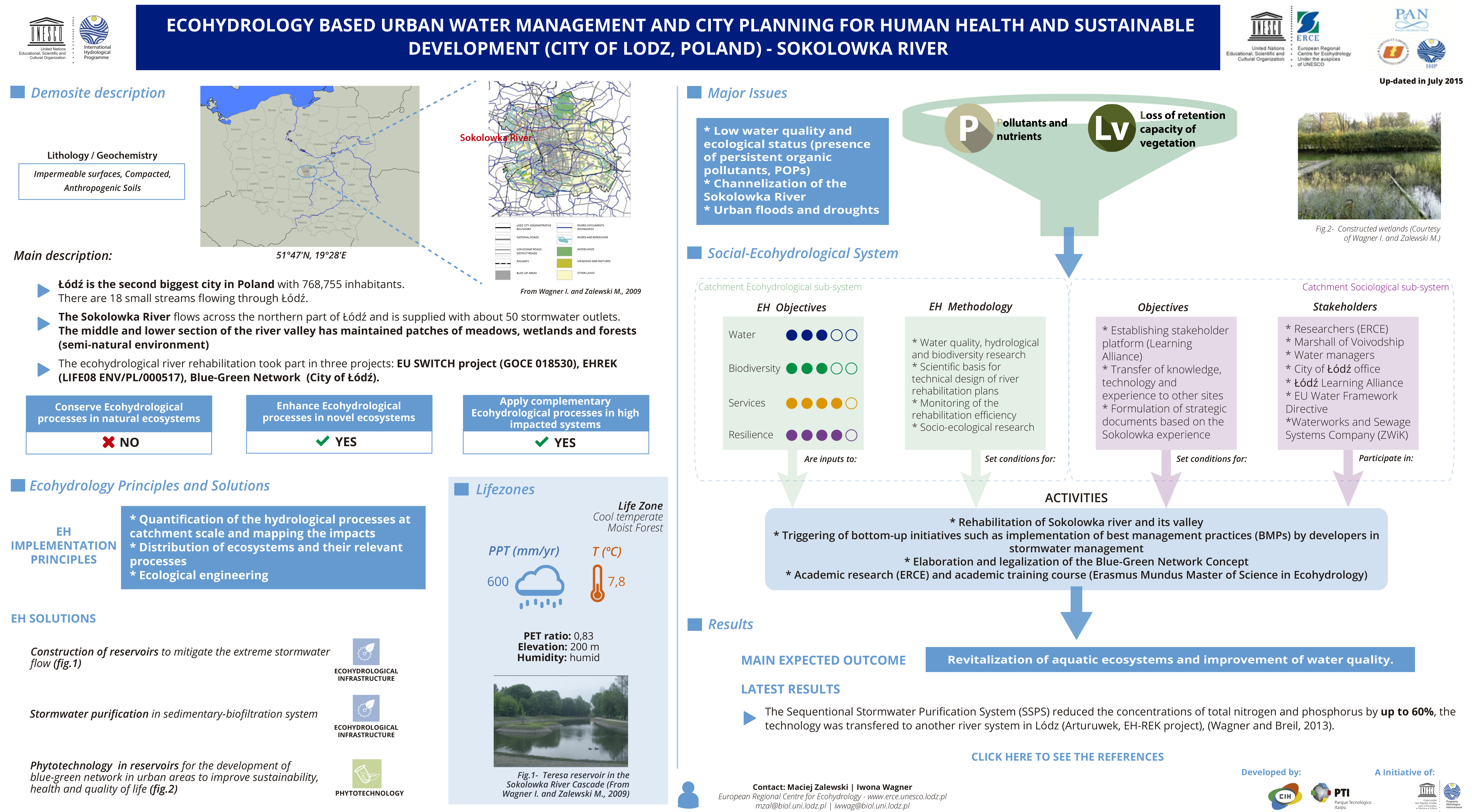
ECOHYDROLOGY BASED URBAN WATER MANAGEMENT AND CITY PLANNING FOR HUMAN HEALTH AND SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT (CITY OF LODZ, POLAND) - SOKOLOWKA RIVER


Description
Location


Sketch

Information about lithology/geochemistry:
Impermeable surfaces, Compacted, Anthropogenic Soils
Main Description
- Łódź is the second biggest city in Poland with 768,755 inhabitants. There are 18 small streams flowing through Łódź.
- The Sokolowka River flows across the northern part of Łódź and is supplied with about 50 stormwater outlets. The middle and lower section of the river valley has maintained patches of meadows, wetlands and forests (seminatural environment)
- The ecohydrological river rehabilitation took part in three projects: EU SWITCH project (GOCE 018530), EHREK (LIFE08 ENV/PL/000517), Blue-Green Network (City of Łódź).
Enhance ecohydrological processes in novel ecosystem
YES
Apply complementary Ecohydrological processes in high impacted system
YES
This table presents the different categories of ecosystem services that ecosystem can provide, divided in:
Provisioning Services are ecosystem services that describe the material or energy outputs from ecosystems. They include food, water and other resources.
Regulating Services are the services that ecosystems provide by acting as regulators eg. regulating the quality of air and soil or by providing flood and disease control.

Local climate and air quality: Trees provide shade whilst forests influence rainfall and water availability both locally and regionally. Trees or other plants also play an important role in regulating air quality by removing pollutants from the atmosphere.

Moderation of extreme events: Extreme weather events or natural hazards include floods, storms, tsunamis, avalanches and landslides. Ecosystems and living organisms create buffers against natural disasters, thereby preventing possible damage. For example, wetlands can soak up flood water whilst trees can stabilize slopes. Coral reefs and mangroves help protect coastlines from storm damage.

Waste-water treatment: Ecosystems such as wetlands filter both human and animal waste and act as a natural buffer to the surrounding environment. Through the biological activity of microorganisms in the soil, most waste is broken down. Thereby pathogens (disease causing microbes) are eliminated, and the level of nutrients and pollution is reduced.
Ecosystem services "that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services". These include services such as nutrient recycling, primary production and soil formation.

Habitats for species: Habitats provide everything that an individual plant or animal needs to survive: food; water; and shelter. Each ecosystem provides different habitats that can be essential for a species’ lifecycle. Migratory species including birds, fish, mammals and insects all depend upon different ecosystems during their movements.
Cultural Services corresponds nonmaterial benefits people obtain from ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, reflection, recreation, and aesthetic experiences.

Recreation and mental and physical health: Walking and playing sports in green space is not only a good form of physical exercise but also lets people relax. The role that green space plays in maintaining mental and physical health is increasingly being recognized, despite difficulties of measurement.

Aesthetic appreciation and inspiration for culture, art and design: Language, knowledge and the natural environment have been intimately related throughout human history. Biodiversity, ecosystems and natural landscapes have been the source of inspiration for much of our art, culture and increasingly for science.

Spiritual experience and sense of place: In many parts of the world natural features such as specific forests, caves or mountains are considered sacred or have a religious meaning. Nature is a common element of all major religions and traditional knowledge, and associated custos are important for creating a sense of belonging.
Lifezones

![]()
PPT(mm/yr): 600.0
![]()
T(ºc): 7.8
| Elevation of demosite: | 200.0 meters above sea level |
| Humidity: | Humid |
| PETr (by year): | 0.83 |
EH Principles
Quantification of the hydrological processes at catchment scale and mapping the impacts
Distribution of ecosystems and their relevant processes (ex: metabolism=water and nutrient uptake and retention; biomass production)
Ecological engineering (integration, dual regulation and biotechnologies in catchment scale for enhancement of ecological potential)
ECOHYDROLOGY ENGINEERING SOLUTIONS
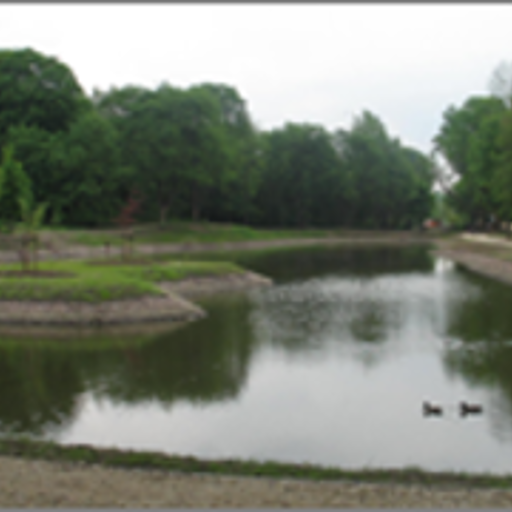
Construction of reservoirs to mitigate the extreme stormwater flow (fig.1)
 Ecohydrological Infrastructure
Ecohydrological Infrastructure
Stormwater purification in sedimentary-biofiltration system
 Ecohydrological Infrastructure
Ecohydrological Infrastructure
Phytotechnology in reservoirs for the development of blue-green network in urban areas health and quality of life (fig.2)
 Phytotechnology
Phytotechnology
Major Issues
- Low water quality and ecological status (presence of persistent organic pollutants, POPs)
- Channelization of the Sokolowka River
- Urban floods and droughts



Expected Outcomes
Revitalization of aquatic ecosystems and improvement of water quality.
Latest Results
- The Sequentional Stormwater Purification System (SSPS) reduced the concentrations of total nitrogen and phosphorus by up to 60%, the technology was transfered to another river system in Lódz (Arturuwek, EH-REK project), (Wagner and Breil, 2013).
Contacts
Maciej Zalewski
- mzal@biol.uni.lodz.pl
- www.erce.unesco.lodz.pl
- European Regional Centre for Ecohydrology
- www.erce.unesco.lodz.pl
Iwona Wagner
- iwwag@biol.uni.lodz.pl
- www.erce.unesco.lodz.pl
- European Regional Centre for Ecohydrology
- www.erce.unesco.lodz.pl
Social ecohydrological system
EH Objectives
EH Methodology
Catchment Ecohydrological sub-system
Objectives
Stakeholders
Catchment Sociological sub-system
Activities