SUSTAINABLE ESTUARINE ZONE MANAGEMENT FOR CONTROL OF EUTROPHICATION, TOXIC BLOOMS AND CONSERVATION BIODIVERSITY IN THE KAŠTELA BAY (CROATIA, ADRIATIC SEA)

Description
Location


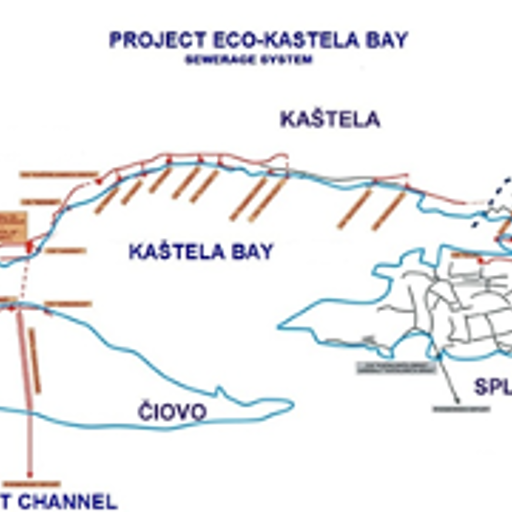
Sketch

Information about lithology/geochemistry:
Kaštela Bay is submerged karst. Muddy sediments settled especially in the east and middle part of the bay, while in the west part prevail sandy sediment (Alfirević, 1980)
Main Description
- Kaštela Bay is one of the largest bays on the eastern Adriatic coast. Most of the freshwater enters the bay from the River Jadro (average annual inflow of 10 m³/s) and from numerous submarine springs.
- Until 2005, the Bay received high quantities of organic matter and nutrients due to the discharge of untreated sewage waters from multiple rivers especially from the river Jadro.
- ECO Project is the Integral Project of Kaštela Bay Protection and it is one of the widest ecological project in the Adriatic and the Mediterranean Seas.
Enhance ecohydrological processes in novel ecosystem
NO
Apply complementary Ecohydrological processes in high impacted system
YES
This table presents the different categories of ecosystem services that ecosystem can provide, divided in:
Provisioning Services are ecosystem services that describe the material or energy outputs from ecosystems. They include food, water and other resources.

Food: Ecosystems provide the conditions for growing food. Food comes principally from managed agro-ecosystems but marine and freshwater systems or forests also provide food for human consumption. Wild foods from forests are often underestimated.
Regulating Services are the services that ecosystems provide by acting as regulators eg. regulating the quality of air and soil or by providing flood and disease control.

Local climate and air quality: Trees provide shade whilst forests influence rainfall and water availability both locally and regionally. Trees or other plants also play an important role in regulating air quality by removing pollutants from the atmosphere.

Carbon sequestration and storage: Ecosystems regulate the global climate by storing and sequestering greenhouse gases. As trees and plants grow, they remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and effectively lock it away in their tissues. In this way forest ecosystems are carbon stores. Biodiversity also plays an important role by improving the capacity of ecosystems to adapt to the effects of climate change.
Ecosystem services "that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services". These include services such as nutrient recycling, primary production and soil formation.

Habitats for species: Habitats provide everything that an individual plant or animal needs to survive: food; water; and shelter. Each ecosystem provides different habitats that can be essential for a species’ lifecycle. Migratory species including birds, fish, mammals and insects all depend upon different ecosystems during their movements.
Cultural Services corresponds nonmaterial benefits people obtain from ecosystems through spiritual enrichment, cognitive development, reflection, recreation, and aesthetic experiences.

Recreation and mental and physical health: Walking and playing sports in green space is not only a good form of physical exercise but also lets people relax. The role that green space plays in maintaining mental and physical health is increasingly being recognized, despite difficulties of measurement.

Tourism: Ecosystems and biodiversity play an important role for many kinds of tourism which in turn provides considerable economic benefits and is a vital source of income for many countries. In 2008 global earnings from tourism summed up to US$ 944 billion. Cultural and eco-tourism can also educate people about the importance of biological diversity.
Lifezones
![]()
PPT(mm/yr): 831.0
![]()
T(ºc): 16.0
| Elevation of demosite: | 0.0 meters above sea level |
| Humidity: | Sub-Humid |
| PETr (by year): | 1.13 |
EH Principles
Distribution of ecosystems and their relevant processes (ex: metabolism=water and nutrient uptake and retention; biomass production)
ECOHYDROLOGY ENGINEERING SOLUTIONS
In 2004, activation of a better sewage treatment system comprising a network of pipelines and pumping stations (fig.1)
 Faunatechnology
Faunatechnology
Follow-up of the microbial food web structure
 Faunatechnology
Faunatechnology
Major Issues
- Increase of nutrient levels and primary production (e.g: red tide blooms)
- Oxygen supersaturation/hypoxia events
- Presence of heavy metals (Hg)
- Intensive industrialized and urbanized area
- Lack of sewage treatments




Expected Outcomes
Significant decrease in plankton abundance and primary production, especially during the summer time (fig.2)
Latest Results
- In the Kaštela Bay, significant changes in food web structure were found in response to changed environmental trophic status before and after activation of new sewage system (Solic M. et al, 2010). The differences also were evident in the absence of nonloricate summer peak and reduction of average nonloricate and tintinnid abundances (N. Bojanic and O. Vidjak, 2010). The most appropriate metrics to assess the degree of eutrophication turned out to be phytoplankton community (Ninčević Gladan et al., 2015)
Contacts
Ivona Marasovic
- marasovic@izor.hr
- www.izor.hr
- Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries
- www.izor.hr
Živana Ninčević Gladan
- nincevic@izor.hr
- www.izor.hr
- Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries
- www.izor.hr
Social ecohydrological system
EH Objectives
EH Methodology
Catchment Ecohydrological sub-system
Objectives
Stakeholders
Catchment Sociological sub-system
Activities